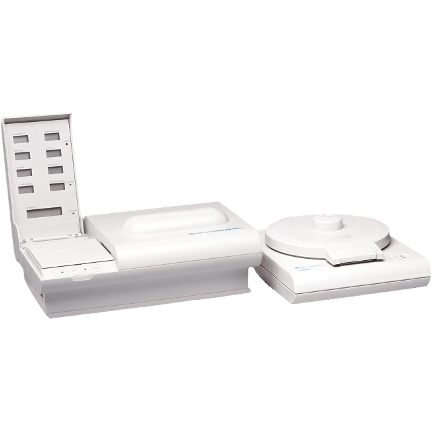
QBC Dry Hematology Analyzers
No liquid reagents
Results in 7 minutes
Finger stick, heel stick or venous draw
How QBC Dry Hematology Systems Work
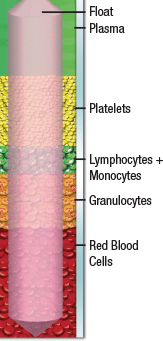
The QBC Tube
The QBC dry hematology technology begins with its unique blood collection tubes. These high grade tubes are internally coated with all necessary stains and reagents and are easily filled with just 65µL of blood from finger sticks, heel sticks, or venous draws.
The QBC centrifuge rotates the tube at 11,000 RPM for approximately 5 minutes. Due to their varying densities, the different components of blood separate into layers during this process.
Due to its specific density, the precision float stretches out the platelet, lymphocyte and monocyte, and granulocyte layers to make these small layers more easily measurable. The precise specific density of the float also allows for the direct measurement of the hemoglobin concentration in the red blood cells.
Click Here for more information regarding Quantitative Buffy Coat Analysis
The Buffy Coat and Float
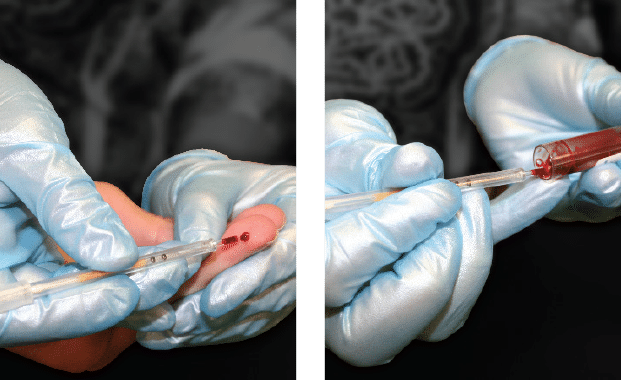
COLLECT BLOOD
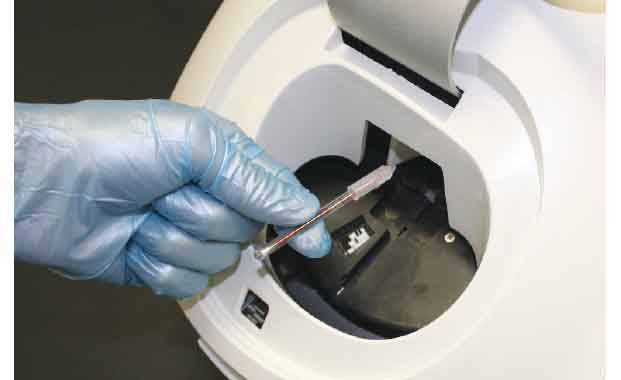
SPIN
ANALYZE
Dry Hematology Analyzers
QBC STAR
- Automatic Operation
- Built-in Centrifuge
- One-Button Operation
QBC Autoread
- Automatic Operation
- External Centrifuge
- Affordable Price
The Science of Dry Hematology
Dry Hematology, which is unique to the Drucker Diagnostics hematology analyzers, performs a complete blood count without the addition of any diluent or liquid reagents. Instead Dry Hematology uses only a precision sample collection tube that is internally dry coated with all necessary reagents, which include Acridine Orange Fluorochrome stain and anticoagulants.
When the hematocrit sample collection tube is filled with approximately 65 microliters of either capillary or venous blood, the dry reagents in the tube mix with the blood sample. A precision mechanical expander (float) in the tube expands the Buffy Coat (white blood cells and platelets) and allows the cells to be digitally imaged. Blue LED’s illuminate the sample, causing the stained bands of cells within the tube to fluoresce different colors. The fluorescent light then travels to the camera, where the digital image is captured and the cell counts, hematocrit, and hemoglobin are measured.


